Service Navigation
Search
Data assimilation is the term given to the process which provides the initial atmospheric conditions, also known as the “analysis”, which is used as the starting point for a model forecast. For this purpose, previous model condition forecasts and real-time observations of temperature, pressure, humidity, wind and precipitation that are distributed irregularly throughout the forecasting region, are combined in such a way as to arrive at a best estimate of the current atmospheric conditions on the model grid.
In the case of ensemble systems such as ICON-CH1-EPS and ICON-CH2-EPS, a host of slightly differing initial conditions is required. This analysis ensemble is calculated at MeteoSwiss with the help of the KENDA (kilometre-scale ensemble data assimilation) system. For high-resolution, convective-scale ensemble forecasting, the analysis ensemble on the ICON-CH1-EPS grid with 1.0-km grid spacing and 80 layers is updated with new measurement data in an assimilation cycle on an hourly basis. The method employed - the Local Ensemble Transform Kalman Filter (LETKF), evaluates observation data and model conditions together with the relevant uncertainties to arrive at the best possible estimate of the current atmospheric conditions. LETKF also provides a multitude of slightly differing analyses that represent the uncertainty of the analysis. Using this analysis ensemble as a basis, the ICON-CH1-EPS forecast is generated once every three hours (00:00, 03:00, ... 21:00 UTC). To obtain the initial atmospheric conditions for the ICON-CH2-EPS forecasts, the analysis ensemble is interpolated every six hours (00:00, 06:00, 12:00 and 18:00 UTC) by upscaling from the higher-resolution ICON-CH1-EPS grid to the ICON-CH2-EPS grid.
Measurement data in the data assimilation process
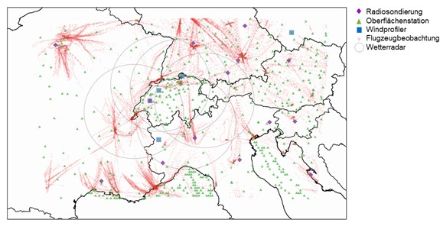
In the assimilation cycle, MeteoSwiss uses all available observations at ground level as well as, and especially, in the atmosphere, in order to be able to describe the atmospheric conditions as accurately and as physically consistently as possible. The KENDA System currently uses measurements from the stations in the ground-level monitoring network, from radiosoundings, aircraft reconnaissance (AMDAR and MODE-S), wind radar and wind lidar data, and notifications from shipping vessels and buoys. Weather radar data, which are particularly valuable for the first few hours of a forecast, are also assimilated with the help of so-called latent heat nudging (LHN).
MeteoSwiss is continually working on integrating new monitoring systems into the data assimilation cycle. For example, the use of humidity profiles from a Raman lidar device is currently being investigated.