Service Navigation
Search
Long-term monitoring of pollen data reveals changes in pollen patterns: early or delayed onset, intensification or amelioration of the pollen season, and the emergence of new allergenic pollen types, such as ragweed. MeteoSwiss measures and analyses the pollen concentrations in the air and identifies the changes in pollen patterns.
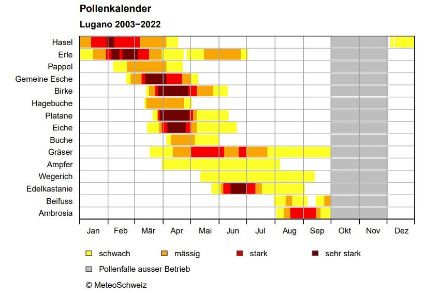
Pollen calendars
Pollen calendars show the average year-round profile of the pollen season for the major allergenic pollen types, and provide an overview at a glance of which pollen types are present when, during the course of the year. They aid in the diagnosis and prevention of pollen allergies. In Switzerland, the pollen season varies from region to region.
Regional pollen calendar brochure
The brochure containing regional pollen calendars provides information on when the pollen season can normally be expected to start in Switzerland, as well as other details such as how long the birch pollen season lasts, etc. Additional graphics and charts give fascinating insights into the subject, under the heading of "What you need to know about pollen".
Reports on the current pollen season
The current pollen season is compared to and ranked in terms of how average values for the pollen season have developed over the long term. These comparisons are published in the seasonal climate bulletin and in the climate report.
Seasonal and annual reports (German, French, Italian)
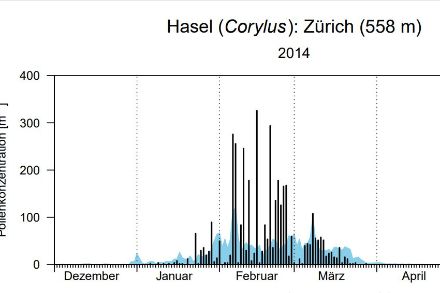
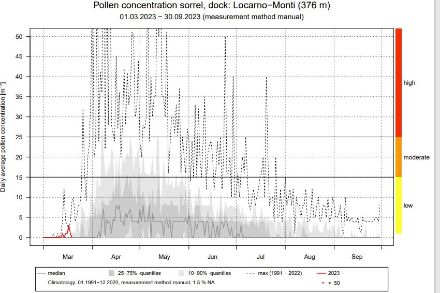
Charts of the current pollen season
The charts are presenting the current year-round profile for pollen data at the various individual pollen monitoring stations in comparison with the long-term averages.