Service Navigation
Search
What is ultraviolet radiation?
UV radiation is a type of short-wave (100-400 nm) electromagnetic radiation that is invisible to the naked human eye. The UV radiation spectrum is divided into three bands: UVA (315-400 nm), UBV (280-315 nm) and UVC (100-280 nm). UVC and 90% of UVB radiation are mostly absorbed by the ozone layer, but also by the oxygen, hydrogen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. The UV radiation that reaches the Earth’s surface consists of UVA and a small proportion of UVB.
There are various environmental factors that influence UV radiation:
- The position of the sun: If the sun is high in the sky, the sun’s rays have a shorter distance to travel through the atmosphere. This means that less of the UV radiation is absorbed and it hits the ground with greater intensity. The intensity not only fluctuates throughout the day, but also over the course of the year. The latitude of a location affects the maximum solar elevation and thus the intensity of the radiation.
- Clouds absorb some of the UV radiation. Sometimes, the intensity of UV radiation can be high despite cloud cover – such as when the layer of cloud is very thin, or when the sun is not covered by the clouds. In addition, the water molecules in clouds can scatter the sun’s rays.
- At higher altitudes, the atmosphere is thinner and less UV radiation is absorbed. The intensity of radiation increases by 10 to 12% for every 1,000 metres.
- Albedo (a measure of how well a surface absorbs or reflects solar rays) also has a significant influence. A snow-covered surface can reflect up to 80% of the solar radiation, whereas most snow-free surfaces absorb a large proportion of the solar radiation.
- The ozone layer, which is located in the stratosphere, absorbs a large part of the UV radiation. Because part of it is destroyed, less UV is absorbed. However, the ozone layer [Internal link: Weather Glossary - Stratosphere and Stratopause] is recovering, enabling better absorption of UV radiation.
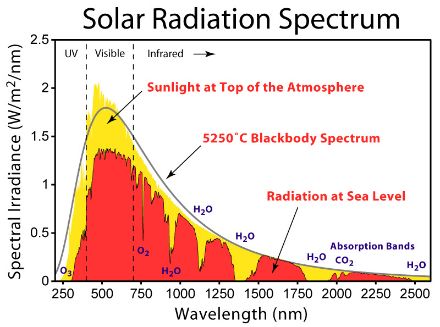
How is the UV index calculated?
A collection of parameters is used to calculate the UV index, including the spectral irradiance of the sun with a wavelength range between 250 and 400 nm. The irradiance of the different wavelengths, from UVB (since UVC does not reach the Earth’s surface) to UVA is weighted based on its potential to cause burns (sunburn or erythema) on the skin. While over 90% of UVB radiation is absorbed by the atmosphere, it is 1,000 times more effective at causing sunburn than UVA radiation. A person’s sensitivity to UV radiation depends on the amount of skin pigmentation. The dose required to have a noticeable effect on the skin (the minimal erythemal dose) for the European population ranges between 200 and 500 joules per square meter.
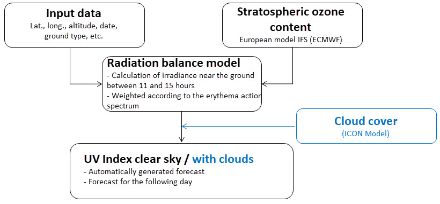
UV-index forecast by MeteoSwiss
MeteoSwiss calculates the UV index daily for the following day. This is an automatically generated forecast based on a radiation model that accounts for the environmental factors mentioned above. Cloud cover is also incorporated into the forecast, and the data is sourced from the ICON model of MeteoSwiss. The index is calculated for the maximum radiation intensity (approximately between 11:00 and 15:00 hours).
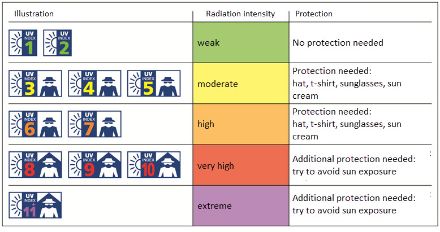
Why do we need a UV index?
The UV-index forecast allows the intensity of solar radiation to be estimated so that people can take appropriate protection measures. The index applies to Switzerland, and it ranges from 1 to 11, the latter indicating extreme radiation intensity (Fig. 3). The recommended protective measures vary with the intensity level. UV rays pose a health risk, with frequent and prolonged exposure leading to faster skin ageing and potentially causing damage that can result in skin cancer. UV radiation can also affect the eyes and weaken the immune system.