Service Navigation
Search
In Europe, there is an increasing need for high-resolution climate monitoring products that extend beyond the national boundaries and span across entire geographical entities (e.g. the Mediterranean area, the Alps, the entire continent). EURO4M has developed new trans-European and high-resolution climate datasets that provide an important basis for the understanding of past climate variations and the planning of adaptations to future climate change.
Differences in national data policies have hampered the exchange of high-resolution climate data and hence the development of transnational datasets. EURO4M was a FP7 Collaborative Project of the European Union that aimed at developing and delivering the best possible gridded climate change time series covering all of Europe. Transnational datasets, user-specific analyses and information bulletins were derived, which support research, authorities and decision making on climate change and its impacts. MeteoSwiss has contributed to EURO4M by focusing on rain and snowfall in the Alps and adjacent lowlands. To this end, it has developed and analyzed a gridded dataset of daily precipitation, covering the entire Alpine region and resolving significant heavy precipitation events between 1971-2008. The unique spatial resolution of this dataset allowed for a rigorous evaluation of new model-based regional reanalyses that were developed within the project.
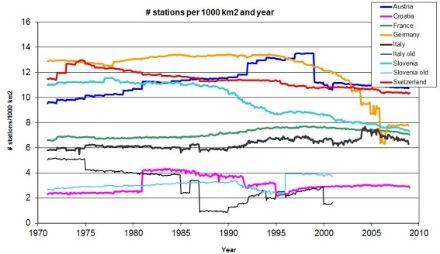
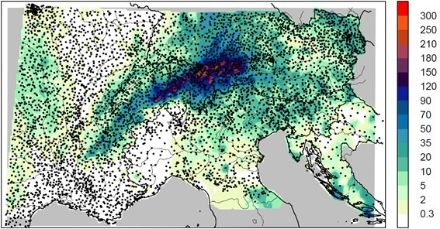
The complex topography of the Alpine ridge is responsible for high precipitation variability at short space scales. Therefore the accuracy of a spatial analysis of climate critically depends on the density of measurements. In EURO4M, MeteoSwiss has compiled all available rain-gauge measurements from national and regional services for the territory from Lower Austria to the Rhone delta and from the Dynaric Alps to Burgundy. The Alpine Precipitation Dataset encompasses data from 8500 weather stations in total, typically 5500 rainfall measurements on average per day. The pooled dataset was rigorously tested for data quality making use of a newly developed spatial consistency test. The new rain-gauge dataset was finally exploited to derive fields of the distribution of rainfall for all days between 1971-2008 on a 5-km grid over the entire Alps. MeteoSwiss can make this grid dataset available to users in research (see Alpine Precipitation Grid Dataset). The MeteoSwiss activities in EURO4M were building on earlier research at the Institute for Atmospheric and Climate Science at ETH Zurich (Frei & Schär 1998).
Frei C. and C. Schär, 1998: A precipitation climatology of the Alps from high-resolution rain-gauge observations. Int. J. Climatol., 18, 873-900.
Isotta, F. A. and Coauthors, 2014: The climate of daily precipitation in the Alps: Development and analysis of a high-resolution grid dataset from pan-Alpine rain-gauge data. Int. J. Climatol., 34, 1657–1675, doi:10.1002/joc.3794.
Isotta, F. A., R. Vogel, and C. Frei, 2014: Evaluation of European regional reanalyses and downscalings for precipitation in the Alpine region. Meteorol. Z., (submitted).
Masson, D., and C. Frei, 2014: Spatial analysis of precipitation in a high-mountain region: Exploring techniques with multi-scale topographic predictors and circulation types. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci., (submitted).
Frei, C., and Coauthors, 2014: Synthesis report of evaluation activities in EURO4M. Deliverable 2.13, Project European Reanalysis and Observations for Monitoring, 13 pp. Available from www.euro4m.eu.
More publications from projects within the NCCR Climate framework