Service Navigation
Search
Introduction
Main purpose of the CN-MET project (Centrale Nucléaire et METéorologie) is to bring up to date the system delivering weather information necessary to the population safety in case of a nuclear hazard. CN-MET represents the coupling of a specifically adapted measurement network and a predictive tool in the form of a fine grid numerical weather prediction model currently developed at MeteoSwiss (COSMO-2). This new tool, calling upon modern measurement and modeling techniques of the atmosphere, represents a solution which will keep all its relevance for the next decades.
In case of a nuclear accident, the necessary atmospheric data used to calculate the diffusion of a contaminated air mass will be provided by a fine grid numerical model, covering the whole Swiss territory. The new measurement network within CN-MET is directly adapted to provide the best information (initial and boundary conditions, and test measurements) for this model. CN-MET not only ensures the emergency preparedness for the concerned population on a local scale, but also enhances it on a regional scale corresponding to the Swiss Plateau.
The measurement network
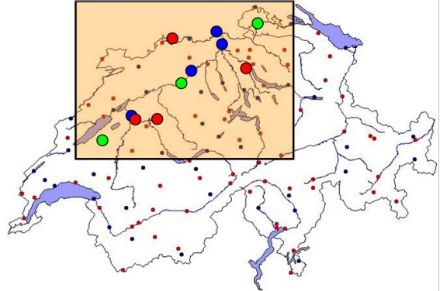
With the CN-MET project a new measurement network (Figure 1) is being set up which includes:
- three remote sensing sites measuring wind and temperature profiles within the planetary boundary layer (PBL), located downwind, upwind and in the center of the domain (data examples cf. Figures 2 and 3),
- surface weather stations from the new SwissMetNet (SMN) network (with additional turbulence measurements) at each of the four nuclear power plants,
- four SMN boundary layer stations in order to add information on wind and temperature measurement in the PBL, which are integrated in the MeteoSwiss measurement network.
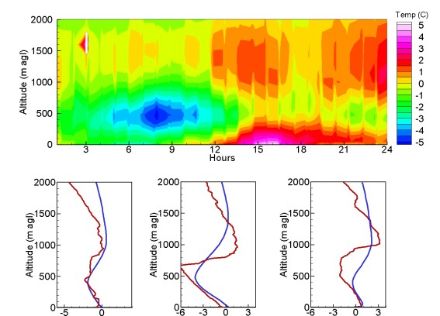
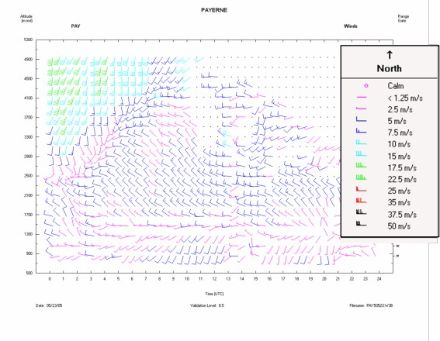
The fine-grid model COSMO-2
As a part of the CN-MET project, a new fine-grid numerical weather prediction model (Figure 4), COSMO-2, is being developed, with the following caracteristics:
- data assimilation from the above mentioned network for initial conditions, thus offering a complete and coherent image of the state of the atmosphere and its evolution (wind, turbulence, precipitation, etc)
- providing input data for the dispersion models in operation at the Swiss Federal Nuclear Safety Inspectorate (ENSI; Eidgenössisches Nuklearsicherheitsinspektorat) for short-distance dispersion calculation around the Swiss nuclear power plants
- providing an 24 hours forecast every 3 hours, with a 10 minutes output time step, for the whole Swiss Plateau
- providing an emergency mode, activated on demand by the ENSI, with an hourly computation of a short-range forecast, in order to satisfy the high requirements of a predictive emergency response tool.
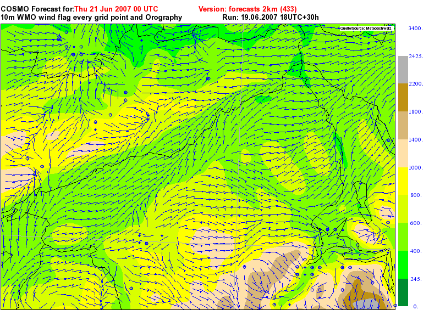
Contacts
- Bertrand Calpini, CN-MET project leader, MeteoSwiss, Aerological Station, P.O. BOX 316, CH-1530 Payerne, Switzerland
- Dominique Ruffieux, responsible for the CN-MET measurement network, MeteoSwiss, Aerological Station, P.O. BOX 316, CH-1530 Payerne, Switzerland
- Philippe Steiner, responsible for the development of COSMO-2, MeteoSwiss, P.O. BOX 257, CH-8058 Zürich, Switzerland
- Olaf Maier, project management, MeteoSwiss, Aerological Station, P.O. BOX 316, CH-1530 Payerne, Switzerland
- Pirmin Kaufmann, CN-MET operating manager, MeteoSwiss, P.O. BOX 257, CH-8058 Zürich, Switzerland